Latest News
EM Research in Malaysia
Jun 14, 2022Agriculture
Effect of Biopriming with Food Waste Bokashi Leachate on Basella rubra L. Seed Germination and Root Growth Performance
Department of Crop Science, Faculty of Agriculture, Universiti Putra Malaysia
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/354264346_Bokashi_leachate_as_a_biopriming_on_Basella_rubra_L_seed_germination_and_root_development
Aquaculture
-
Animal Husbandry
-
Compost/Waste Treatment
Landscape Waste Composting with the Aid of Effective Microorganisms using Mechanical Crusher Machine
Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia, Pagoh Campus
https://publisher.uthm.edu.my/ojs/index.php/jaita/article/view/6474
Compost Physical Properties Study on Degradation of Poultry Manure Composting in Closed-Aerated Composter
Department of Chemical Engineering Technology, Faculty of Engineering
Technology, Universiti Malaysia Perlis
https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1757-899X/932/1/012012/meta
Performance analysis of effective microorganisms on chicken manure composting
Centre for Biofuel and Biochemical Research (CBBR), Department of Chemical Engineering,
Universiti Teknologi Petronas
https://li01.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/sehs/article/view/239847
Effects of Fermentation on the Nutritional Composition, Mineral Content and Physical Characteristics of Banana Leaves
Faculty of Agro-Based Industry, Universiti Malaysia Kelantan
http://myscholar.umk.edu.my/handle/123456789/483
Compost Physical Properties Study on Degradation of Poultry Manure Composting in Closed-Aerated Composter
Department of Chemical Engineering Technology, Faculty of Engineering Technology, Universiti Malaysia Perlis
https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1757-899X/932/1/012012/pdf
Effect of pretreatments on compost production from shredded oil palm empty fruit bunch with palm oil mill effluent anaerobic sludge and chicken manure
Department of Biological and Agricultural Engineering, Universiti Putra Malaysia
http://psasir.upm.edu.my/id/eprint/72441/
Evaluation of Effective Microorganisms on home scale organic waste composting
Journal of Environmental Management
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0301479717303602
In-vessel co-composting of yard waste and food waste: an approach for sustainable waste management in Cameron Highlands, Malaysia
International Journal of Recycling of Organic Waste in Agriculture volume 6, pages149–157 (2017)
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40093-017-0163-9
The Effectiveness EM Mudball and Banana Peels for Textile Wastewater Treatment
Department of Water and Environmental Engineering, University of Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia, Johor Bahru.
https://www.matec-conferences.org/articles/matecconf/pdf/2017/01/matecconf_encon2017_01009.pdf
Producing Fertilizer from Food Waste Recycling using Berkeley and Bokashi Method
Universiti Teknologi MARA (Terengganu)
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/303325296_Producing_fertilizer_from_food_waste_recycling_using_berkeley_and_bokashi_method
Water Treatment
The natural way for water quality improvement using effective microorganism
Faculty of Civil Engineering, Universiti Teknologi MARA Shah Alam
https://www.inderscienceonline.com/doi/abs/10.1504/IJEE.2021.118462
Verifying the applicability of SWAT to simulate fecal contamination for watershed management of Selangor River, Malaysia
Research Centre for Environmental Quality Management, Graduate School of Engineering, Kyoto University, 1-2 Yumihama, Otsu 520-0811, Japan
Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Malaya
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0048969721001418
Investigation on the Efficiency of Effective Microorganisms for Polluted Water Treatment
Department of Applied Sciences, UCSI University, W. P. Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
https://ojs.wiserpub.com/index.php/AMTT/article/view/683
Improvement of Water Quality using Effective Microorganisms
Faculty of Civil Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia
https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Improvement-of-Water-Quality-using-Effective-WahidAzman/f7044d207541fd7698cfc37c9d68ab7633a3c837
A Study on the Effectiveness of Biofilter Based on Effective Microorganism (EM) and Empty Fruit Bunch (EFB) for Water Quality Improvement: An Application in Open Channel System
Faculty of Civil Engineering and Earth Resources, Universiti Malaysia Pahang
http://umpir.ump.edu.my/id/eprint/2891/
Effective Microorganisms (EM) Technology for Water Quality Restoration and Potential for Sustainable Water Resources and Management
Universiti Sains Malaysia,Penang,
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/232805617_Effective_Microorganisms_EM_Technology_for_Water_Quality_Restoration_and_Potential_for_Sustainable_Water_Resources_and_Management
Construction
Microstructure and Strength Properties of Sustainable Concrete Using Effective Microorganisms as a Self-Curing Agent
Taif University, Taif, Saudi Arabia & University Teknologi Malaysia (UTM)
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/362863998_Microstructure_and_Strength_Properties_of_Sustainable_Concrete_Using_Effective_Microorganisms_as_a_Self-Curing_Agent
Effective Microorganism Solution and High Volume of Fly Ash Blended Sustainable Bio-Concrete
Department of Physics and Laser Centre, AOMRG, Faculty of Science, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
https://www.mdpi.com/2313-7673/7/2/65
Evolution effect of nano-glass powder on the strength performance and microstructure of high-volume fly ash-based concrete incorporated with effective microorganisms
institute for Smart Infrastructure and Innovative Construction, School of Civil Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4042530
Biogenic approach for concrete durability and sustainability using effective microorganisms: A review
School of Civil Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 Johor, Malaysia
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S095006182031669X?via%3Dihub
Effect of effective micro-organism on temperature variation in concrete
Hossain, Md. Awlad (2019) Effect of effective micro-organism on temperature variation and properties of concrete. Masters thesis, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Faculty of Engineering - School of Civil Engineering.
http://eprints.utm.my/id/eprint/81123/
Introducing Effective Microorganism as Self-curing Agent in Self-cured Concrete
UTM Construction Research Centre, Institute for Smart Infrastructure and Innovative Construction, School of Civil Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1757-899X/849/1/012081
Influence of marine kaolin mortar mixed with effective microorganism on external heat transfer
UTM Construction Research Centre, Institute for Smart Infrastructure and Innovative Construction, School of Civil Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1757-899X/849/1/012043
Green technology and sustainable urban drainage systems using eco-composite porous concrete: A preliminary study
UTM Construction Research Centre, Institute for Smart Infrastructure and Innovative Construction, School of Civil Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
http://eprints.utm.my/id/eprint/88900/
Fresh and hardened properties of concrete containing effective microorganisms
UTM Construction Research Centre, Institute for Smart Infrastructure and Innovative Construction, School of Civil Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1755-1315/220/1/012050
Development of low thermal mass cement-sand block utilizing peat soil and effective microorganism
Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Universiti Teknologi PETRONAS
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/321076945_Development_of_low_thermal_mass_cement-sand_block_utilizing_peat_soil_and_effective_microorganism
Compost Physical Properties Study on Degradation of Poultry Manure Composting in Closed-Aerated Compost
Department of Chemical Engineering Technology, Faculty of Engineering Technology, Universiti Malaysia Perlis
https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1757-899X/932/1/012012/meta
etc
Effective Microorganisms as Halal-Based Sources for Biofertilizer Production and Some Socio-Economic Insights: A Review
Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, Universiti Putra Malaysia (UPM), Serdang 43400, Selangor, Malaysia
Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, University of Tabuk, Tabuk P.O. Box 741, Saudi Arabia
https://www.mdpi.com/2304-8158/12/8/1702
Peat soils stabilization using Effective Microorganisms (EM)
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science
https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1755-1315/140/1/012088
Production of effective microorganism using halal-based sources: A review
School of Material Engineering University Malaysia Perlis (UniMAP)
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/272688884_Production_of_effective_microorganism_using_halal-based_sources_A_review
Potential of Mud Ball from Biolarvacide from Fermented Malaysia's Ulam Herbs
Center of Excellence Geopolymer& Green Technology (CEGeoTech), School of Material Engineering, Universiti Malaysia Perlis
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/246547647_Potential_of_Mud_Ball_From_Biolarvacide_From_Fermented_Malaysia's_Ulam_Herbs
Lee Pineapple Co Pte Ltd Effluent Water Treatment
Feb 4, 2021.jpg)
.jpg)





Yes everyone, EMRO Malaysia is back with an EM event. Yayyyyyyy!!!!!!!
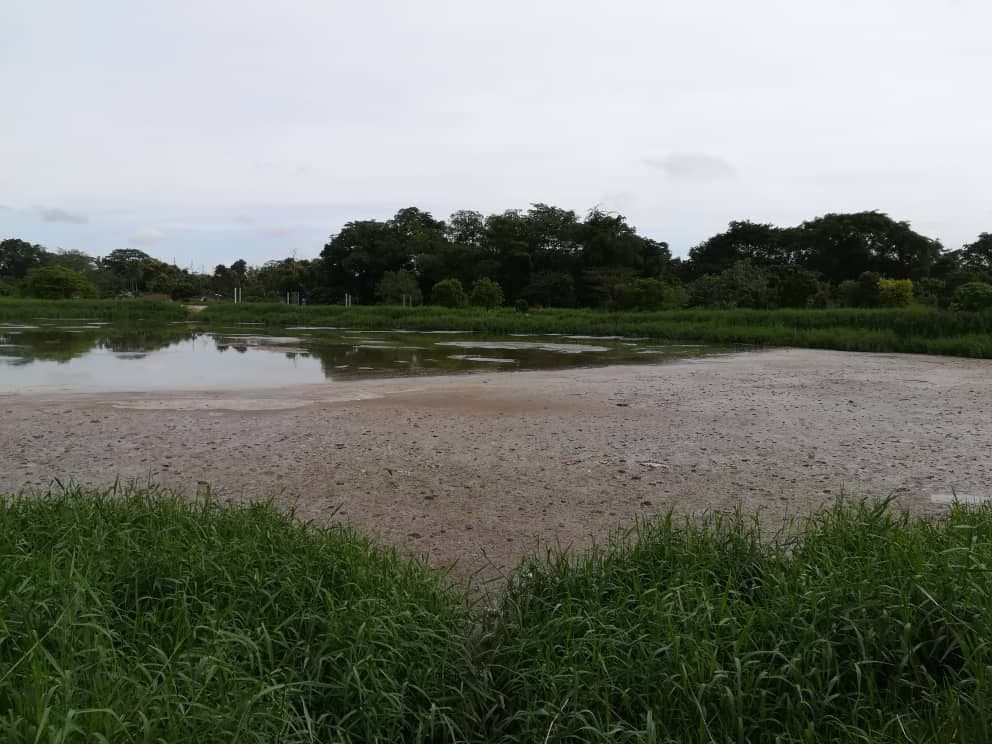
The Lee Pineapple Co Pte Ltd has been operating since 1931 and has the support of the Malaysian Pineapple Industry Board (Johor). Recently their water treatment-effluent pond has been giving off an offensive smell after the monsoon season, unfortunately disturbing nearby residents. This problem had occurred back in 2006. This time, the issue has resurfaced due to the latest monsoon season.
We gave the following EM Application suggestion:
1. EMAS (EM Activated Solution) ---------50L per day -10L/hour for 5 hours during production day
2. PB (Phototropic bacteria)-------------5L per week -1L per day during production day
3. EM Mudball-----------------15,000 pcs EM mudball (twice per year)
We look forward to see positive feedback from EM Application!
#EMROMalaysia #EMGreenlife #EMROJapan #EMTechnology #Effectivesmicrobes
Malaysian Pineapple Industry Board (Johor)
http://www.mpib.gov.my/lembaga-perindustrian-nanas-malaysia/
Lee Pineapple Co Pte Ltd
https://leepineapple.com/
October 30, 2015 - EM-Cera Sticker
Oct 30, 2018

Stickers infused with EM™ Ceramics. With two designs you can choose from, you can stick it on any surface you like.
The Effect of E-Cera Sticker indicated by LFA Electromagnetic Wave Measurement
Semiconductors are widely used for televisions, computers, mobile phones, microwaves ovens and etc. Electromagnetic wave emitted from them is said to have bad effect on the human body. E-Cera Sticker contains fine powder of EM Ceramics sealed by the special technique and lessen resonate in semiconductors. According to the result of LFA Electromagnetic Wave Measurement, although using mobile phones usually shows a lowering of immunity, E-Cera Sticker have an effect on heightening immunity.
.png)
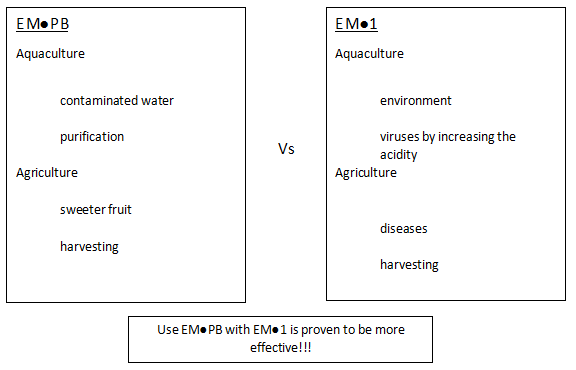
October 30, 2016 - EMí˝PB
Oct 30, 2018Photosynthetic Bacteria
Photosynthetic Bacteria’s obtain their energy from light and can be easily found in nature. Besides being non-toxic and harmless to environment, they synthesise useful substances from the secretions of roots, organic matter and/or harmful gases (e.g. hydrogen sulphide) by using sunlight and the heat of soil as sources of energy. They contribute to a better use of sunlight or, in other words, better photosynthesis. The metabolites developed by these micro-organisms are directly absorbed into plants. In addition, these bacteria increase the number of other bacteria and act as nitrogen binders.
Application
In Agriculture it helps to increase the amount of photosynthetic bacteria in soil, promoting healthy plant, sweeter fruit and bushier flowers.
Dilute 1 litre of EMí˝PB in 500 litre water and use in the agriculture irrigation system or by spraying over the crops leaves and soil. Apply it to crops once in every two weeks. Combination with EMí˝1 or EMAS and EM Bokashi is more effective.
In Aquaculture, EMí˝PB helps in water treatment and purification by decomposing the organic matter that cause water contamination and aquaculture problems. Combination with EMí˝1 or EMAS is more effective.
Dilute 1 litre of EMí˝PB in 1000 litre water and use it directly once in one or two weeks in the aquaculture systems. Combination with EMí˝1 is more effective.
Difference between EMí˝PB and EMí˝1
November 7, 2016 - EM movie "Sosei" (Revival) in Johor
Oct 30, 2018Movie title : Sosei (English and Chinese subtitle)
date and time: 18 Nov 2016 10:30 am - 12:00 am
Venue: Fo Guang Shan (conference hall)
PTD 70521 (LOT 111561)
Jalan Persisiran Sutera Danga,
Taman Sutera Utama
81300 Johor Bahru,
Johor, Malaysia.
It's free ! Limited seats available.
If you are interested, pls feel free to contact us immediately!
EMRO Malaysia Sdn Bdh
77 Jalan Sutera Tanjung 8/2
Taman Sutera Utama
81300 Skudai, Johor Bahru,
Johor, Malaysia
tel: 07 562 1195
Sosei official website:
http://officetetsushiratori.jp/sosei/en/index.php




January 21, 2017 - 35th Dr. Higa EM Anniversary
Oct 30, 2018
.jpg)

It was established to achieve the goal of Dr. Teruo Higa under his guidance to solve worldwide problems in agriculture, environment and human health.
EM was originally developed by Dr. Teruo Higa in Okinawa, Japan in 1982, and it has penetrated all over the world since then, thanks to the support from a lot of farmers, and EM users in environment and many other fields.
More than 3 million liters are sold every year, and this year celebrated the 35th anniversary since the development of EM, which shows the effectiveness of original EMRO EM.
EMRO group continues to improve and develop further to meet the evolving users’ demands in various fields.

March 3, 2017 - EMRO first set foot in Brunei
Oct 30, 2018
EM Talk and EM Workshops were given at The Core University of Brunei Darussalam (UBD) and IBTE Wasan Vocational School.
We also visited and discussed on EM application at the pond of biggest Talapia fish breeder and supplier in Brunei.
Thank you very much YESINV Management Services for this invites and opportunities. We will keep in touch and hope to establish more collaboration in the future.”
March 13, 2017 - EM Talk and EM Mudballs activities in SJKC Woon Hwa, Kangkar Pulai, Skudai
Oct 30, 2018
March 29, 2017 - EM Talk and EM Mudball activities in SJKC Rawang Selangor (29 March 2017)
Oct 30, 2018
April 2, 2017 - EM Mudball throwing at Skudai river
Oct 30, 2018
2200 pcs of Mudball was thrown.
On the next day, 3 April 2017, an article about this event was publish on SIN CHIEW DAILY local newspaper.
We invite all Facebook followers to join the same event at Kota Tinggi, Johor this Saturday. Details as below.
EM Mudballs Throwing
Venue: Titian Laksamana Kota Tinggi ( Jambatan Gantung)
Time : 9.30am till 11.30 am
June 24, 2017 - EMRO-ZENXIN Agroworld Booth
Oct 30, 2018


Congratulations to our partner ZENXIN for winning the "Outstanding Fertilizer Quality Product Award" for their Midori organic fertilizer !

Midori organic fertilizer
-product certified by EMRO and NASAA (National Association for Sustainable Agriculture Australia)
-organic fertilizer with Effective Microorganisms® for crop cultivation and soil supplement
-enhances better rooting Nutrients in easily available amino acid forms and improves crop, quality & yields
Midori organic fertilizers are available in our shop / online store !
April 13, 2018 - EM RECIPE
Oct 30, 2018(**Activated EM•1 is called EM Activated Solution “EMAS “)
Materials
- Water 400 ml
- Molasses 20 - 25 ml (or brown sugar 20 - 25 gm)
- EM•1 20 - 25 ml
- 500-ml bottle
- Pour 400 ml of water into a measuring cup.
- Add 20 - 25 ml of molasses (or 20 - 25 gm of brown sugar). Mix well.
- Add in 20 - 25 ml of EM•1®. Mix well.
- Pour all contents into the plastic bottle. Make sure to leave about 10% air space.
- Keep the bottle tightly closed and leave in a warm place (i.e. 20 - 40oC) for 7 – 10 days.
- Loosen the cap a few times over the 10 days to release pent-up gas.
- When gas formation stops, the fermentation process is complete.
- Store in a cool dark place.
Points to note:
- Check to make sure the cap is always closed tightly for both EM•1 and EMAS. When air enters during the fermentation stage, unwanted microbes can enter and begin putrefying the contents.
- DO NOT use a glass bottle for making EMAS as the pent-up gas may lead to an explosion.
- To check for quality, ensure that the pH is below pH 3.6. The smell should be sweet-sour.
- After opening the bottle of EM•1, white flakes may appear on the surface of the liquid. This is yeast and is harmless.
- Discard if the pH rises above 4 or if there is a foul smell.
- To ensure the quality, we do not recommend to use a 2nd generation of EMAS or further generation.
• EM likes warm conditions.
A suitable temperature for fermentation (propagation) of EM•1 is from 30°C to 40°C. In the winter, and other times when the temperature is low, after making the Activated EM•1 (dissolving the molasses in hot water), place the EM next to a radiator, space heater, or other warm device, or even wrap it in a blanket or an insulator, in order to promote EM fermentation.
When is Activated EM•1® ready to use?
Activated EM•1 is ready to use, 7 - 10 days after preparing it, when the pH of Activated EM•1 drops below 3.6 (ideally it has a pH between 3 - 3.5), and when it has a sweet-sour smell and has changed color from black to dark brown. However, please note that there will be some variation in the results of the fermentation of Activated EM•1 due to factors such as; the quality of the water and molasses, the amount of EM•1 and molasses, and temperature differences (water during mixing, room temperature).
USE:
Ideally, it is best to use Activated EM•1 within a week after Activated EM•1 is ready (after the pH is below 3.6). The effective microorganisms in Activated EM•1 are very active and powerful during this period. You can use Activated EM•1 for up to one month after it is ready. However, the microbial effects of Activated EM•1 are not as great as when it is "young".
Storage
Activated EM•1 should be kept in an expandable air-tight container to keep it anaerobic. Store Activated EM•1 at room temperature 20°C to 30°C. Refrigeration is not necessary. In containers that are not totally airtight, a white layer of yeast bacteria may form on the surface. Since this may lead to putrefaction, remove the layer as needed and transfer to a container that can be closed tightly. If stored Activated EM•1 has a foul smell or the pH rises above 4.0, the solution could be contaminated with undesirable microbes and should be discarded. It is fine to pour this material on a long-term compost pile.
Uses for Activated EM•1:
From domestic use to Cleaning up the environment
- Improving soil quality for healthy plants.
- Eliminating foul odor.
- Keeping your drain clean.
- EM•1 eliminates odor so, it can be used for cleaning in the home.
- Dilute EM•1 or Activated EM•1 with water (1:500 dilution) then use it for cleaning.
- A half cup in the washing machine can help clean the clothes.
- The EM•1 in the water draining into your pipes will work on cleaning the sewer lines.
- A half cup in a vaporizer will remove odors in the home (cigarettes, wet dog smell, food).
- Clean the bathroom with it too. Have spray bottle handy and spray into the sink, shower, and toilet after each use. (1:500 dilution).
✔Use quality EM・1
✔Clean air-tight container
✔Clean water
✔Sweet and uncontaminated molasses.
✔keep in a warm place during fermentation
ideal temperature is 20-35íŠ
✔Keep anaerobic condition
Checklists for Quality EMAS:
Fermentation period - 7-10 daysúĘdepends on temperatureúę
- pH - Should drop to below 3.6
- Smell - Sweet-sour fermentation smellúĘUnpleasant smell means failure of the processúę
- Color - Dark brown turns into a lighter brown
- Gas formation - Generally stops when fermentation is completed
2. How to prepare EM™ Mudballs
Materials
- Soil. It is usually better to use clay-soil that can easily be formed into balls.
- Activated EM•1.
- Molasses (At 10% the volume of the Activated EM•1)
- EM Bokashi.
- Use EM Mudballs in river bottoms and mud flats where slime has accumulated. Generally, use one EM Mudball for each square meter (1m X 1 m) of the polluted area.
- Use EM Mudballs once each season until results are seen.
- Cleaning up oceans, rivers, lakes and ponds requires the application of EM into the water through a variety of methods. It is recommended that Activated EM•1 also be regularly applied into the water to supplement the use of EM Mudballs.
For 10,000 EM Mudball (100m X 100m area)
-1500kg Soil- Clay-like-soil. Easy to form balls.
-150kg EM Bokashi
-500L Activated EM•1 (EMAS).
- EM Ceramics Powder may be added- Optional
-Charcoal powder (5-10%) -Optional
Note:
Since the water content of the soil used will vary, the amount of Activated EM•1 (EMAS) will vary as well. As a general rule, though, if for instance you produce 15 liters of material you will need approximately 1 liter/quart of Activated EM•1 (EMAS). Always be sure to have enough Activated EM•1 (EMAS) on hand in case it is needed. If you use it up, you can add extra water instead (don’t be afraid to use a lot of Activated EM•1).
The amount of optional EM Ceramics Powder will be between 0.1% of the total amount. For example, for 10 liters of material this will equal 10 gram of EM Ceramics Powder.
Agriculture April 13, 2018 - EM Application
Oct 30, 2018WHY WE NEED TO USE EM IN AGRICULTURE?
Dr. Higa upholds a completely different concept of agriculture, opposed to the current agriculture practice- To achieve not only food production but also to protect the environment, resources and human health while being economically successful.
Throughout 20 years of proper application, EM Technology™ is proven to be economical and effective in promoting a sustainable and environmentally friendly agriculture. Its benefits include:-
- Decomposition of organic matter (including organic wastes and residues)
- An alternative to chemical fertilizers
- Recycling and increasing availability of plant nutrients
- Fixation of atmospheric nitrogen
- Suppression of soil-borne pathogens
- Solubilisation of insoluble nutrient sources
- Production of polysaccharides and overall rich microflora to improve soil aggregation
- Promotes photosynthesis and strengthens the vigor of plants, thus increasing their ability to withstand drought, floods, and temperature extremes.
- Increases soil temperature through microbial activity, which enables greater cultivation in colder regions.
- Improves soil aggregation, permeability, and water holding capacity—thus reducing overall water usage.
- Helps prevent the erosion of fertile topsoil—and can even convert desert and sodic environments into arable land.
- Detoxifies, conserves, and improves the overall quality of water and the runoff tributaries.
In short, the key to abundant agriculture is to make effective microorganisms dominant. With the application of EM, native microorganisms, most of which are opportunistic, are stimulated and work in cooperation with EM in a good way for environment.
HOW TO APPLY EM IN AGRICULTURE:
1. In seed and seeding treatment
-soak the seed into EMAS (1:500 dilutions) for half to one hour and then dry in room temperature (not under direct sunlight)
-For vegetative propagators such as potatoes, sugar cane or ginger: soaking time is 5 minutes.
2. Plant Transplantation
-spray EMAS(1:200 dilution) before transplanting to facilitate growth.
.png)
3. Watering
-Waters your plant once a week with 1:500 EMAS to Water dilution or through existing irrigation system in agriculture.
4. Prevention of pest and disease.
-Spray 1:200 of EM5 to Water Dilution to plant once a week
-For soil problem, apply 1:200 EMAS directly to the soil once a week
April 13, 2018 - Animal Husbandry
Oct 30, 2018WHY WE NEED TO USE EM IN ANIMAL HUSBANDRY?
The intensive industrialization of animal farming practice worldwide poses serious pollution and health issues to the livestock and workers in the farms. The odour coming from urine and faeces of the animals produce ammonia gas, a putrefactive oxidative substance which causes respiratory stress for both the workers and the animals living under such conditions.
EM™ with its strong antioxidant effect has shown significant results in breaking up ammonia, accelerating the conversion of animal waste into manure compost, and prevent noxious odour. In the livestock industry where animals are raised in overcrowded conditions, spraying of EM at animal pens promotes the growth of other beneficial microbes, therefore improving the environment within the pens which in turn leads to a reduction of stress on the animals, higher quality milk, meat, eggs, and the suppression of diseases. EM•1® can also be mixed in the drinking water and feeds to promote overall health of the animals.
Benefits of EM for animal husbandry:
- Suppresses foul odour in livestock sheds and septic tanks
- Reduces stress factors for animals - decreases flies, ticks and other harmful insect populations
- Enhances animal health – improve immunity against diseases
- Increases quality of animal products and enhances shelf life
- Improves animal fecundity
- Getting high quality manure
- Reduces use of regular medicines, antibiotics and disinfectants
.jpg)
Spray EM
.png)
EM Reduce ammonia level
HOW TO APPLY EM IN ANIMAL HUSBANDRY:
1. Drinking
-Apply EM•1 (1:500 Dilution into drinking water).
-Drinking water should be change every day if EMAS is added into it.
2. Feeding
-Mix 1% to 3% of EM Bokashi into their feed once a week to increase intestinal micro flora. Hence increasing the digestive process and increase animal’s health
3. Spraying
-Apply 1:200 EMAS to Water Dilution around the shed and the wall once a week to reduce smell.
-if the smell still continue, Dilute 1:500 EM PB to Water and spray.
-Spraying onto the animals themselves does not cause any harm.
April 13, 2018 - Aquaculture
Oct 30, 2018WHY WE NEED TO USE EM IN AQUACULTURE?
As a result of industrialization, the water body of our ocean is heavily contaminated by the discharge of industrial and household wastes. The application of EM can significantly decompose these pollutants by promoting the growth of beneficial microbes which causes pollutants to ferment and break down rather than putrefy, creating an environment for the growth of aquaculture resources.
.png)
Benefits of using EM in Aquaculture
- EM improves the productivity and the quality of harvested products.
- EM improves the water quality (Turbidity, DO, PH, etc.) and reduce the production of harmful gases such as ammonia, hydrogen sulphide and methane.
- Reduce the quantity of sludge
- Reduce the population of pathogenic microbes in the water.
- Reduce the frequency of recycling water-lowering the cost.
- Reduce the use of using antibiotics.
HOW TO APPLY EM IN AQUACULTURE
1. Feeding.
-Mix 1L EMAS to 10kg of feed every day. No fermentation needed.
2. Water Condition and sludge reduction
-apply 1:10,000 EMAS/PB to pond water volume
April 13, 2018 - EM for Composting
Oct 30, 2018WHY WE NEED TO USE EM IN COMPOSTING
Composting is an environmentally conscious method of creating organic fertilisers out of organic wastes. At present, the fundamental challenge for composting is in properly aerating the piles, which is labour intensive and therefore expensive. Using conventional composting methods, piles must be turned frequently or they risk becoming putrefying, which produces foul smelling gases such as ammonia and mercaptans, attracts numerous flies, and yields potentially disease-inducing product.
The addition of EM•1 can help to overcome these challenges by eliminating the odour and establish beneficial microbial growth by preventing the anaerobic pockets from putrefying. When carefully managed, EM•1 has the potential to reduce the frequency of turning the piles, saving both time and money.
Food Waste
Using EM™ you can recycle food waste to make valuable fertilizer for your gardens and plants. EM™ helps to speed up the natural composting process — without the negative side-effects of foul odours and pests. Adding compost to the soil and then mulching it will help to hold in moisture, requiring less watering, keep weeds down, and provide a home for worms and microbes.
The benefits of using EM made food waste compost include:
- EM compost enhances decomposition and produces nutrient-rich soil humus, perfect for enhancing the garden
- Reduces odour for undetectable indoor composting
- Significantly reduces disease-producing pathogens resulting from compost putrefaction
- Produces nutrient-rich compost
- Increases beneficial microbial activity in the soil, therefore enhances better root development
- Enhances resistance of plants to stress and reduces soil borne pathogens
- Safe and environment friendly as it is organic and biodegradable.
- Sprinkle a small amount of EM Bokashi on the bottom of Composting Bin.
- The food waste is break into small pieces to ease the breakdown process.
- Food waste is in well drained condition. Not wet.
- Every time food waste is added, EM Bokashi is added as well.
- Push down the food waste and bokashi to make it compact.
- Close the lid tightly to prevent contamination.
- Drained the Food waste juice collected frequently. Can be dilute (1:500) and use to waters plant or Pour into the drain to release EM into the environment. Do not keep the juice collected-Must be use immediately.
- After the bucket is full, let it sit, tightly closed, for at least one week to ferment. (Allowing it to sit longer is fine, but makes sure the materials are not too moist to cause rotting and odor.)
- After another two weeks, you can plant directly into the soil.
.jpg)
Points to note:
- Check to make sure the lid is always closed tightly. When air enters during the fermentation stage, unwanted microbes can enter and begin putrefying the food waste.
- White mold is good. This is beneficial fungus that helps produce antibiotics (to suppress pathogens) and antioxidants. This fungus will also help with water retention in the soil.
- Green or Black mold are not good. These are putrefying fungus and are usually the result of air infiltration, excess moisture, and/or not enough EM Bokashi.
.jpg)
April 13, 2018 - Water TREATMENT
Oct 30, 2018The self-purification power of water works well under the indigenous ecosystem functioning properly with a rich aquatic ecosystem pyramid. In polluted water with sludge accumulating at the bottom, water’s self-purification power decreases as a result of dominance by putrefactive microorganisms. This leads to decrease of nutrition necessary for ecosystem to function and keep their purification.
When applied to polluted and putrefactive water, EM helps revive the ecosystem by reducing sludge and foul odours. Nevertheless, the application of EM will not create crystal clear water as what can be done by chemical means. Depending on the water condition, the amount and frequency of EM’s application could vary.
.png)
1. Apply 1:10,000 EMAS/PB to pond water volume
2. For River, apply 1 EM Mudball per 1 square metre.
.png)
April 13, 2018 - Landscape ĘC Soil Treatment
Oct 30, 2018The rapid industrialization and intensities in chemical usage has resulted in depleting nutrients in the soil. In this regard, EM™ has shown significant effect as a catalyst to naturally detoxify and enrich the soils and restore its microbial diversity. This in turn stimulates growth, yield, shelf-life and overall nutritional quality of the plants while reduces the growth of weeds and herbivore insects, thus gradually eliminating the need for toxic herbicides, pesticides, and synthetic fertilizers.
The use of EM™ accelerates the soil building process and promotes beneficial microbial communities. Soil building process revolves around soil aggregate formation. EM•1® produces high levels of polysaccharides and other beneficial enzymes and organic acids that help build stable aggregate and soil structure. Improved soil aggregate stability reduces soil erosion and run-off. Soils are better able to absorb and retain moisture, as well as cycle nutrients.
April 13, 2018 - EM™ for Construction
Oct 30, 2018Recently the issue of "Sick House Syndrome" has arisen, and there is a greater awareness of the materials used in construction. If one inhales fumes from paint, new building materials and adhesives, one can get sick. Mould and house mites are also a factor in this illness.
In the construction industry, it is possible to enhance the functionality of materials though adding EM™ products. The building's durability will be improved, and in actual construction it's been shown that the damage caused by adhesives and organic solvents can be reduced. At present EM•1® and EM-X® ceramics are being used in concrete in actual construction, and numerous buildings and houses have been completed implementing the use of EM Technology™ in construction materials right from the design. The best example is the EM™ Wellness Center in Okinawa, Japan. Instead of tearing down the decrepit building, the concrete building materials were revitalized through the use of EM Technology™, and the Center itself has successfully become a leading architectural model.
.png)
.png)
Effects of EM™ for construction:
- Strengthen the building physically and extend the life of the building
- Reduces sick house syndrome
- Creates the atmosphere good for human health


































































